User Experience Changes Between WSL 1 and WSL 2 Contributors [](https://github.com/mscraigloewen "mscraigloewen") This page goes over the user experience differences between WSL 1 and the WSL 2 preview. The key changes to be aware of are: - Place files that your Linux apps will access in your Linux root file system for faster file performance speed - In initial builds of the WSL 2 preview you will need to access network applications using an IP address and not using localhost And below is the full list of other changes that you may notice: - WSL 2 uses a VHD to store your files and if you reach its max size you may need to expand it - When starting, WSL 2 will now use a small proportion of memory - Cross OS file access speed will be slower in initial preview builds ## Place your Linux files in your Linux root file system Make sure to put the files that you will be accessing frequently with Linux applications inside of your Linux root file system to enjoy the file performance benefits. These files have to be inside of the Linux root file system to have faster file system access. We have also made it possible for Windows apps to access the Linux root file system (like File Explorer! Try running: `explorer.exe .` in the home directory of your Linux distro and see what happens) which will make this transition significantly easier. ## Accessing network applications In the initial builds of the WSL 2 preview, you will need to access any Linux server from Windows using the IP address of your Linux distro, and any Windows server from Linux using the IP address of your host machine. This is something that is temporary, and very high on our priority list to fix. ### Accessing Linux applications from Windows If you have a server in a WSL distro, you'll need to find the IP address of the virtual machine powering your distro and connect to it with that IP address. You can do that by following these steps: - Obtain the IP address of your distro by running the command `ip addr` inside of your WSL distro and finding it under the `inet` value of the `eth0` interface. - You can find this more easily by filtering the output of the command using grep like so: `ip addr | grep eth0`. - Connect to your Linux server using the IP you found above. The picture below shows an example of this by connecting to a nodeJS server using the Edge browser. [](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/media/wsl2-network-w2l.jpg) ### Accessing Linux network applications from Windows Accessing Windows applications from Linux To access a Windows network application you'll need to use the IP address of your host machine. You can do so with these steps: - Obtain the IP address of your host machine by running the command `cat /etc/resolv.conf` and copying the IP address following the term `nameserver`. - Connect to any Windows server using the copied IP address. The picture below shows an example of this by connecting to a python server running in Windows via curl. [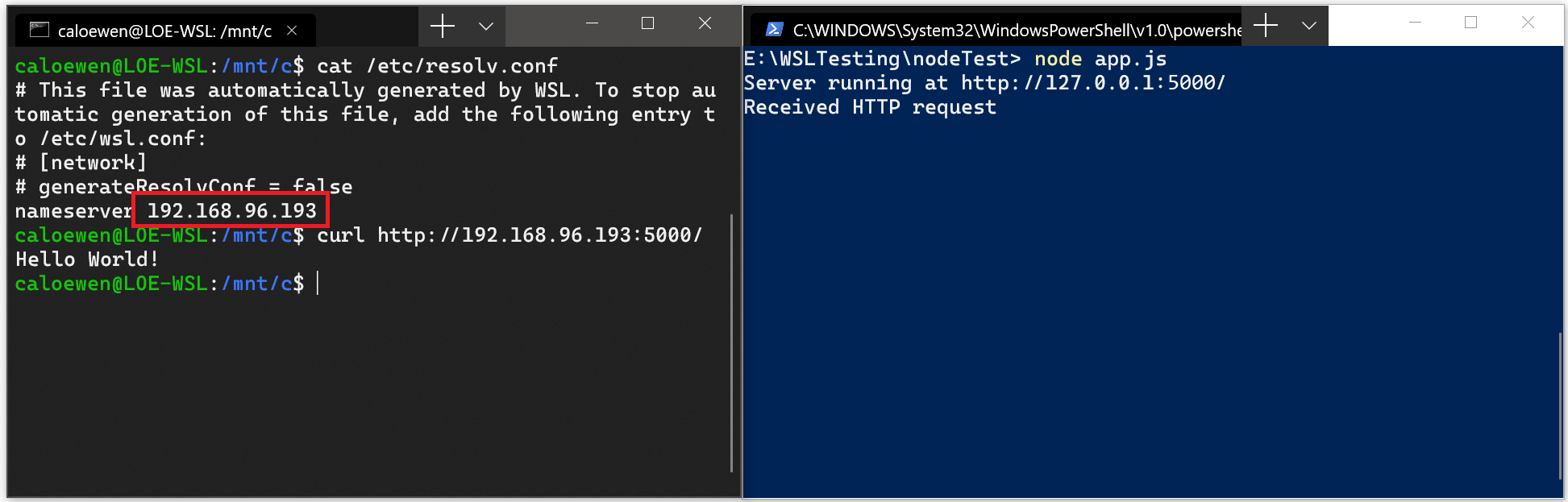](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/media/wsl2-network-l2w.png) Accessing Linux network applications from Windows ### Understanding WSL 2 uses a VHD, and what to do if you reach its max size WSL 2 stores all your Linux files inside of a VHD that uses the ext4 file system. This VHD automatically resizes to meet your storage needs. This VHD also has an initial max size of 256GB. If your distro grows in size to be greater than 256GB you will see errors stating that you've run out of disk space. You can fix these by expanding the VHD size. Instructions on how to do so are below: 1. Terminate all WSL instances using the `wsl --shutdown` command 2. Resize your WSL 2 VHD by completing the following commands - Open a command prompt Window with admin privileges and run the following commands: - `Select vdisk file="<pathToVHD>"` - `expand vdisk maximum="<sizeInMegaBytes>"` 3. Launch your WSL distro 4. Make WSL aware that it can expand its file system's size - Run these commands in your WSL distro: - `sudo mount -t devtmpfs none /dev` - `mount | grep ext4` - Copy the name of this entry, which will look like: /dev/sdXX (with the X representing any other character) - `sudo resize2fs /dev/sdXX` - Make sure to use the value you copied earlier, and you may need to use: `apt install resize2fs`. ### WSL 2 will use some memory on startup WSL 2 uses a lightweight utility VM on a real Linux kernel to provide great file system performance and full system call compatibility while still being just as light, fast, integrated and responsive as WSL 1. This utility VM has a small memory footprint and will allocate Virtual Address backed memory on startup. It is configured to start with a small proportion of your total memory. ### Cross OS file speed will be slower in initial preview builds You will notice slower file speeds compared to WSL 1 when accessing Windows files from a Linux application, or accessing Linux files from a Windows application. This is a result of the architectural changes in WSL 2, and is something that the WSL team is actively investigating on how we can improve this experience. [User Experience Changes Between WSL 1 and WSL 2](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/wsl2-ux-changes "User Experience Changes Between WSL 1 and WSL 2")